Interoperability
Interoperability and Integration Engineering
Skill 2 of 9 | Pillar I: Autonomous System Architecture
The connective tissue that transforms isolated agents into cohesive enterprise AI ecosystems. Without interoperability, even the most capable individual agents remain siloed—unable to collaborate, share context, or integrate with the systems where real work happens.
The Integration Imperative
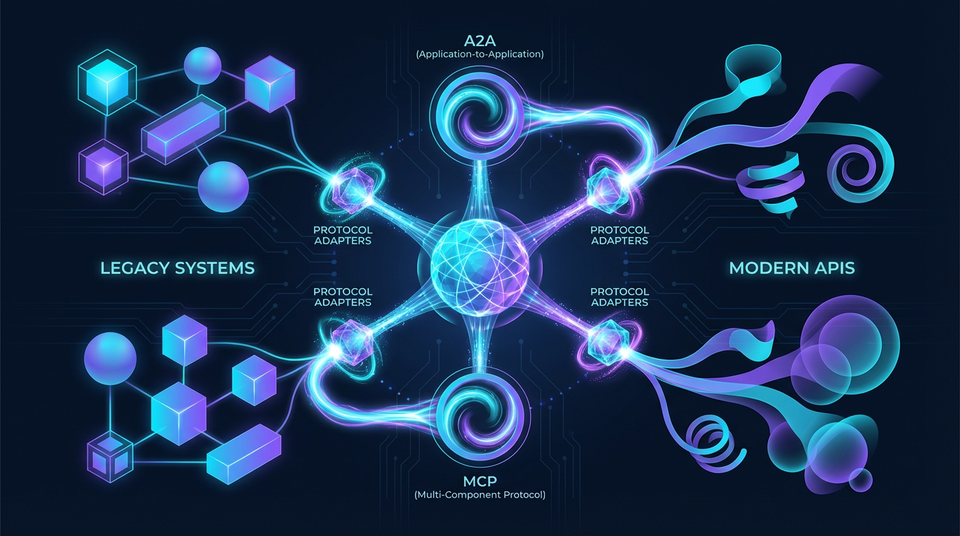
No agent operates in isolation. Every production agentic system must connect with other agents, legacy systems, databases, APIs, and human workflows. The ability to build these bridges—reliably, securely, and at scale—separates functioning enterprise AI from impressive demos.
Consider the reality of most organizations: decades of accumulated infrastructure, multiple cloud providers, legacy systems running critical business logic, and now agents from different vendors with different protocols. The integration challenge isn't just technical—it's architectural. How do you create coherent systems from heterogeneous components?
This is why interoperability is the second foundational skill, immediately following orchestration. You can design perfect agent workflows, but if those agents can't communicate with each other and with existing systems, the workflows remain theoretical.
The principle-based approach is essential here. Protocol standards evolve rapidly—A2A, MCP, and other standards are still maturing. Organizations that learn specific protocol implementations will constantly be relearning. Those who understand the underlying integration patterns can adapt to any protocol.
Protocol Standards and Adaptation
The first competency within interoperability is understanding the emerging protocol landscape and building systems that can adapt as standards evolve.
Agent2Agent Protocol (A2A)
The Linux Foundation's Agent2Agent protocol represents the industry's first serious attempt at standardized agent collaboration. At its core, A2A enables agents to discover each other's capabilities and collaborate on tasks without prior coordination.
The Agent Card specification is central to A2A. Each agent publishes a machine-readable description of its capabilities, inputs, outputs, and constraints. Other agents can query these cards to understand what an agent can do before attempting to delegate tasks.
This semantic capability discovery changes how multi-agent systems are built. Rather than hardcoding agent relationships, systems can dynamically discover and utilize agents based on their declared capabilities. A new specialized agent can be added to an ecosystem and immediately become discoverable to other agents.
The task lifecycle management in A2A standardizes how agents hand off work, report progress, and return results. This enables agents from different vendors to participate in the same workflows—a critical capability for enterprise deployments.
Model Context Protocol (MCP)
Anthropic's Model Context Protocol takes a different approach, focusing on how agents access tools and data sources. MCP's client-host-server topology separates the agent (client) from the systems that provide capabilities (servers), with a host managing the connection.
The power of MCP lies in its approach to enterprise data exposure. Organizations can create MCP servers that provide controlled, secure access to their data and systems. Agents connect through standardized interfaces without needing custom integration code for each data source.
The "Golden Skills" concept in MCP encourages organizations to identify their most valuable capabilities and expose them through well-designed MCP servers. This creates reusable building blocks that any MCP-compatible agent can leverage.
For RAG systems, MCP provides standardized patterns for document retrieval, search, and context injection. Rather than building custom integrations for each knowledge source, agents use MCP's standardized interfaces.
OpenAPI and Tool Definition Standards
Before agent-specific protocols, OpenAPI established the standard for API specification. This legacy remains valuable—many tools and services are exposed through OpenAPI-documented REST APIs.
Understanding OpenAPI 3.x specifications enables agents to consume existing APIs without custom integration. JSON Schema provides the type system for validating inputs and outputs. Contract-first development ensures API changes don't break agent integrations.
The versioning strategies in OpenAPI are particularly important. Enterprise systems evolve, and agents must handle API version changes gracefully. Breaking changes require careful management; non-breaking extensions should be automatic.
Multi-Protocol Translation and Adaptation
The reality is that no single protocol will dominate. Organizations need agents that can work with A2A, MCP, OpenAPI, and proprietary protocols simultaneously.
Protocol adapters bridge between standards. An adapter translates between A2A's capability discovery and MCP's tool exposure, allowing agents using either protocol to collaborate. Mediation layers handle schema mapping when data representations differ.
This adapter pattern is crucial for future-proofing. When new protocols emerge—and they will—organizations with well-designed adapter layers can add support without redesigning their agent architectures.
Legacy System Integration
The second competency addresses the reality that most enterprise value lives in systems built years or decades ago. Modern agents must work with this infrastructure.
REST and SOAP API Integration
Many enterprise systems expose APIs, but the protocols and patterns vary widely. SOAP services from the early 2000s use XML and WSDL. REST APIs vary in their adherence to REST principles. GraphQL offers flexible querying but requires different client patterns.
The adapter layer pattern isolates agents from these variations. Agents communicate with adapters using standardized interfaces; adapters translate to whatever protocol the legacy system requires. This prevents legacy coupling from infecting agent code.
For ERP systems, CRM platforms, and custom enterprise applications, adapter layers provide the stable interface agents need. The adapter handles authentication, error translation, rate limiting, and protocol-specific quirks.
Enterprise Database Integration
Sometimes agents need direct database access rather than going through APIs. This creates both opportunities and risks.
The query generator pattern has agents describe what data they need in natural language or structured queries, and a specialized component generates safe SQL. This prevents SQL injection and enables fine-grained access control.
Read-only access is the default—agents should rarely have write permissions to production databases. When writes are necessary, they should be scoped to specific tables and operations, with full audit logging.
Connection pooling, query optimization, and timeout handling are essential. Agents that hold database connections too long or run expensive queries can impact production system performance.
Message Queue and Event Stream Integration
Enterprise systems increasingly communicate through event streams and message queues. Agents must participate in these patterns.
Integration with Kafka, RabbitMQ, and similar systems allows agents to consume events and produce responses asynchronously. This fits naturally with agentic workflows that may take significant time to complete.
Event sourcing compatibility means agents can work with systems that represent state as event streams. The agent consumes events, maintains its own view, and produces new events as it takes action.
Back-pressure handling is critical. Agents must gracefully handle situations where they can't keep up with incoming messages, either by scaling up or by communicating capacity limits to upstream systems.
Human-in-the-Loop Integration
Many enterprise workflows require human approval for significant actions. Agents must integrate with approval systems rather than bypassing them.
Integration with ServiceNow, Jira, Slack, and similar platforms enables agents to request approval through established channels. The approval request includes context the human needs to make a decision.
The pattern is straightforward: agent reaches a decision point, submits approval request, waits for response, continues or takes alternative action based on the response. The complexity is in the integration—matching approval requests to responses, handling timeouts, managing escalation.
This human-in-the-loop integration is essential for compliance workflows, high-stakes decisions, and situations where organizational policy requires human oversight.
Security and Trust in Interoperability
The third competency addresses the security challenges that arise when systems cross trust boundaries.
Mutual Authentication and Identity Verification
When two agents collaborate, each must verify the other's identity before sharing information. This is particularly important in cross-organization scenarios.
Mutual TLS (mTLS) provides strong cryptographic verification. Each agent has a certificate; connections require both parties to present valid certificates. This prevents impersonation and ensures encrypted communication.
Token-based authentication using OAuth 2.0 or OIDC provides flexible authorization. Tokens can carry scopes that limit what actions an agent can take, and they expire automatically.
Agent identity goes beyond authentication—it includes verification that the agent is what it claims to be. Certificate chain validation, trust anchors, and revocation checking prevent compromised agents from participating in sensitive workflows.
Data Lineage and Toxic Flow Analysis
In multi-agent systems, tracking where data came from and where it went is essential for security and compliance.
Data lineage graphs show the flow of information through the system. When an agent produces an output, the lineage shows which inputs contributed to that output. This enables compliance monitoring—you can verify that sensitive data wasn't inappropriately combined or exposed.
Toxic flow analysis identifies patterns where information crosses security boundaries inappropriately. If an agent receives sensitive customer data and sends it to an external service, toxic flow analysis flags this violation.
Audit trails capture all cross-system interactions. In regulated industries, these trails are mandatory; everywhere else, they're invaluable for debugging and incident response.
Capability-Based Access Control
Rather than all-or-nothing access, capability-based systems grant specific, scoped permissions.
When an agent needs to access a resource, it requests a capability token describing the access it needs. The token grants only that specific access—read a particular table, call a specific API method, access data for a particular customer.
This implements least privilege at a granular level. Even if an agent is compromised, its capability tokens limit the damage it can cause.
Zero trust architecture assumes no agent should be trusted by default. Every access request is verified, every capability is scoped, every action is logged.
The Principle-Based Transformation
Learning specific protocols and APIs creates fragile expertise. Protocols evolve, APIs change, and new standards emerge. The organizations that succeed are those that understand the underlying principles.
API design principles apply regardless of whether you're using REST, GraphQL, or gRPC. Versioning strategies, backward compatibility, and schema evolution are universal concerns.
The adapter pattern appears in every integration architecture. Understanding anti-corruption layers and protocol translation prepares you for any integration challenge.
Authentication and authorization patterns—OAuth, OIDC, capability tokens—transcend specific implementations. The cryptographic and security principles remain constant.
Transferable Competencies
Mastering interoperability requires proficiency in several foundational areas.
API Design encompasses REST, GraphQL, gRPC, and versioning strategies. Understanding API design principles enables you to both consume and create well-designed interfaces.
Data Modeling using JSON Schema, Protocol Buffers, and canonical data models ensures consistent data representation across system boundaries.
Event-Driven Architecture principles including event sourcing, CQRS, and message queue patterns enable integration with modern distributed systems.
Authentication and Authorization skills covering OAuth, OIDC, mTLS, and capability tokens are essential for secure cross-system communication.
Distributed Tracing using OpenTelemetry and correlation IDs enables debugging and monitoring across system boundaries.
Common Pitfalls
Tight coupling to protocols mixes business logic with protocol-specific code. When protocols change, everything breaks. Keep protocol handling at the edges of your system.
Ignoring versioning assumes APIs won't change. They will. Plan for version evolution from day one.
Weak authentication trusts agents without verification. In multi-agent systems, impersonation is a real threat.
Missing error handling assumes integrations always succeed. Network failures, timeouts, and service unavailability are normal. Design for graceful degradation.
Synchronous-only integration blocks on every external call. Asynchronous patterns provide better throughput and resilience.
Implementation Guidance
For architects, design canonical data models for cross-system integration. Define adapter layer boundaries and responsibilities. Specify authentication and authorization mechanisms. Plan for protocol versioning and evolution. Document security boundaries and trust domains.
For developers, implement protocol adapters with clear interfaces. Use schema validation at integration boundaries. Add comprehensive error handling and retry logic. Implement distributed tracing for cross-system calls. Test with protocol version mismatches.
For organizations, establish integration standards and patterns. Create adapter layer reference implementations. Invest in API management and gateway infrastructure. Implement centralized authentication and authorization. Build integration testing environments.
Looking Forward
The integration landscape continues evolving. Universal agent protocols—likely building on A2A and MCP—will become standards. Semantic interoperability will enable agents to reason about capability compatibility automatically. Self-describing APIs will reduce manual integration work.
The organizations that master interoperability principles today will adapt smoothly as these evolutions occur. Those locked into specific protocol implementations will face constant migration projects.
The bottom line: Interoperability is the connective tissue that transforms isolated agents into cohesive systems. Master the principles, and you can integrate anything with anything.
Next Skill: Observability — Making agent behavior transparent and debuggable
Back to: The Nine Skills Framework | Learn
Subscribe to the Newsletter → for weekly insights on building AI systems that actually work.
